Vitamin D is produced by the skin from direct sunlight so, it is essential that the skin is exposed to sunlight few minutes every day to obtain the recommended daily allowance of vitamin D.
The most important function of vitamin D is to absorb calcium from food and regulate the amount of calcium and phosphate in the body. Most of the calcium is used to keep teeth, bones, and muscles healthy.
Vitamin D is also needed to send messages along the nerves and to help muscles, such as the heart muscles, to contract.
Vitamin D deficiency causes rickets in children, a condition in which the bones are soft, brittle and bend. In adults it leads to osteomalacia, a condition which causes muscle weakness and bone pain.
Researchers believe that vitamin D plays a key role in boosting immune system by fighting the infections caused by bacteria and viruses. It is believed that it is a contributing factor in reducing the risk of getting colon cancer.
Research also suggests that it plays a role in prevention and treatment of health conditions like Type 2 Diabetes, hypertension and multiple sclerosis.
What is the difference between vitamin D2 and D3?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin. The type of vitamin D that body makes when exposed directly to the sunlight is known as vitamin D3, or cholecalciferol.
This type of vitamin D is created when the ultraviolet in the sunlight reacts with a type of cholesterol that is found under the skin naturally.
Even though most of the vitamin D is formed through the exposure of the skin to sunlight there are some foods that do contain vitamin D naturally. This type of vitamin D is known as vitamin D2, or ergocalciferol.
What foods provide vitamin D?
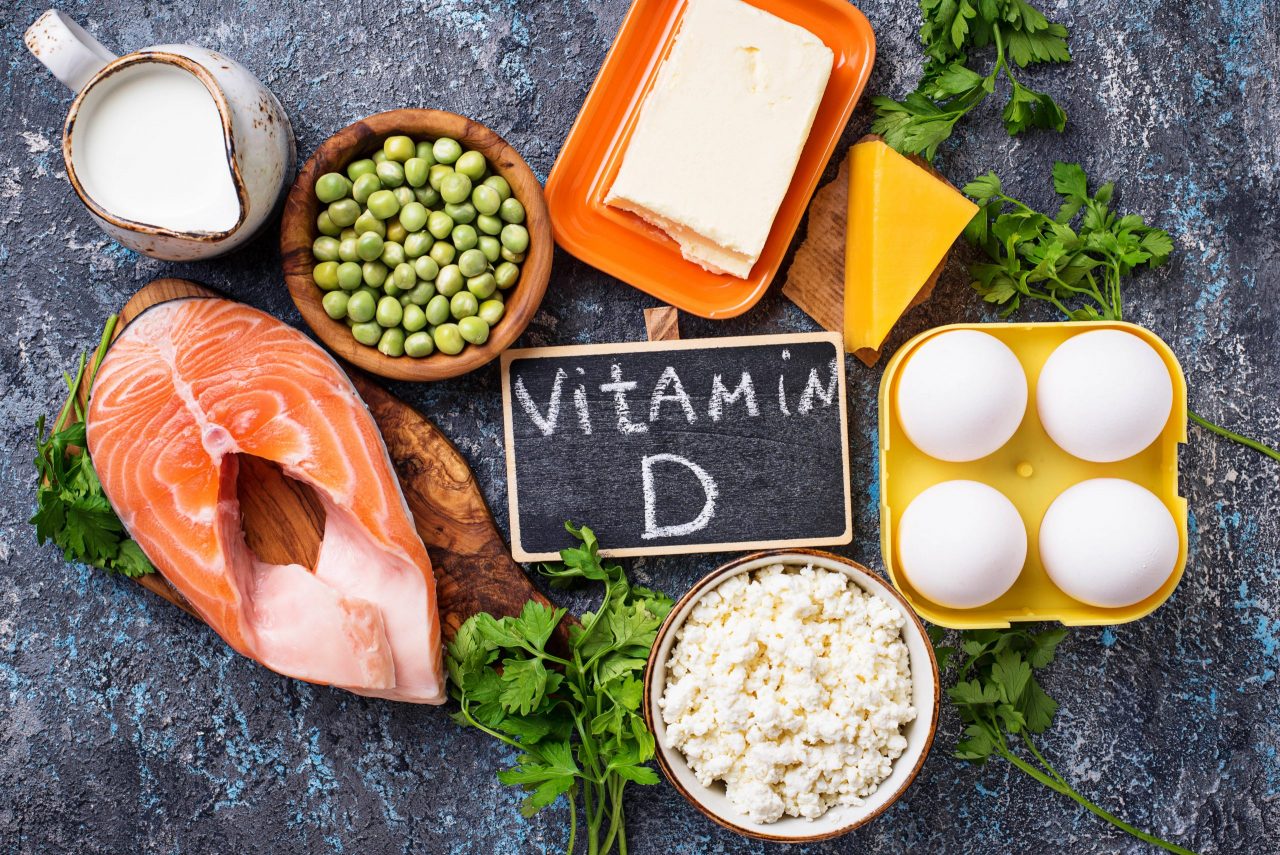
Vitamin D is found in very few numbers of foods.
- Fish such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, hilsa, trout, sardines and sword fish.
- Cod liver oil
- Mushrooms are the only plant-based food source
- Liver, Cheese and egg yolk
- Fortified milk and curd/yoghurt
What are the normal levels of vitamin D?
Normal levels of vitamin D in healthy people are from 30 nmol/L (12 ng/mL) to 125 nmol/L (50 ng/mL). Anything less than 12ng/mL is vitamin D deficiency and above 150ng/mL is toxic.
25-hydroxyvitamin D test is the best way to check vitamin D levels in your body.
How much vitamin D should I take?
Bone pain and muscle weakness can mean you have vitamin D deficiency. Low vitamin D levels can cause heart problems, asthma in children and cancer.
If you have any vitamin D deficiency symptoms and you think your body is not making enough vitamin D from sunlight, then you need to speak to your doctor about taking vitamin D supplements.
Average daily recommended amount of vitamin D you need each day depends on your age and health conditions.
- Babies from Birth to 12 months need 10 mcg (400 IU) a day
- Everyone aged 1–70 years need 15 mcg (600 IU) a day
- Teenagers 14–18 years need 15 mcg (600 IU)
- Elderly over 70 years need 20 mcg (800 IU) a day
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women need 15 mcg (600 IU) a day
If you have vitamin D deficiency, then your doctor might prescribe 4000 IU daily.
If you decide to take vitamin D supplements, 10mcg(400IU) a day is sufficient for many people. Vitamin D supplements are available in the pharmacies as tablets, capsules and injections.
Causes of vitamin D deficiency
In general, young people and healthy male have sufficient levels of vitamin D. Vitamin D deficiency caused by number of factors.
- If you are a vegan, then there is a chance of getting less vitamin D
- If you are old or have kidney problems, then your kidneys are less able to convert vitamin D to its active form.
- If you are obese, then your body fat prevents vitamin D from getting into the blood.
- If you have any diseases like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease, then your body can’t handle fat properly and vitamin D needs fat to be absorbed.
- If you have dark skin, then pigment melanin reduces the absorption of vit D.
You cannot overdose on vitamin D from sunlight but taking too many Vitamin D supplements for a long time can build up too much calcium in the body, causing a condition called hypercalcaemia. This can cause bone weakness and damage to the heart and kidneys.
If you have any health conditions, then you must consult your doctor before taking vitamin D supplements.
You can take 10mcg (400 IU) of vitamin D daily to keep your bones and muscles healthy.
Some news reports suggest that vitamin D can be taken for preventing and treating COVID-19.
Researchers from Queen Mary University of London are conducting clinical trials to give a definite answer to the question whether vitamin D offers protection against Covid-19. People participating in this study will be given high doses of vitamin D daily for six months.
Close to 30 studies show that optimal blood levels of vitamin D (75-150 nmol/L) reduces covid-19 risks: reduced risk of infection; reduced risk of severe disease; reduced risk of dying.
There is little to be lost and a huge amount to gain by taking a decent daily dose of vitamin D3 (say 1,000 IU for children and 4,000 IU for adults).